Information Warfare #3
2 des. 2013Repetition from last lecture:
- Cyber warfare: Can be offensive and defensive, legal caution must be taken when dealing with offensive actions. Is cyber deterrence possible? [paper cited: Cyber Deterrence: An Old Concept in a New Domain by Michael J. Philbin]
- Hacktivism as a special case of activism
- Categories of attack: DoS, defacement, system modification, theft, high energy weapons, electromagnetic radiation interception.
We discussed COTS, the Common Off The Shelves solutions, standardized solutions that can be bought versus in-house development. Open source vs closed source, probability of large open source code bases being reviewed, availability for scientific testing and development. Organizations tend to outsource because doing the job internally is expensive in terms of knowledge needed and time consumption. Security certification was popular for a while but the cost is too high and the scheme too static. Testing makes it very expensive.
Information management is about making well informed decisions fast by means of sharing of information. This is achieved by improving processes, culture and technology so that information can be shared efficiently cross geographical, organizational and personal boundaries.
- Leadership: Define goals so that the information collected and used is targeted to achieve a common goal. Discover unrealized potential in individuals and groups. Aggregate situation awareness. How information is valued, what to collect and what to protect.
- Organization: Information must be targeted to people to avoid overload. A good balance between organization and free information flow is needed.
- Learning: Learning and knowledge have an individual and a group perspective.
- Technology: Technology is an enabler so that information more easily can cross boundaries and be reused, but require a fitting culture in order to be effective.
What is the value of information? Information archived vs. actively used. Who has access to it. When is knowledge created? Decision points, written down knowledge, tacit knowledge. Balance resources used on protecting the information in relation to what it is worth.
- Time, content and context: Time is how time critical the information is. Must we act on it now or within a year? Content is the area it can be understood in, typically because of specialization. Marketing, production, personnel and research were mentioned as examples. Context is the importance of the information as in low tactical or high strategical. Information that can turn a war is more important than information that can turn a battle.
- Risk, value and importance: Risk is a relationship between threats and vulnerabilities, value is the surplus after expenses is covered and importance is the relationship between time and context.
CKO is a theory that summarizes the course and the letters stand for Coherent Knowledge-based Operations. It merges the concepts of knowledge management, network-centric business/operations and information warfare in order to control the information environment, or in other words to increase an organizations competitive advantage while at the same time measures are taken to reduce competitors advantages. Limited resources such as personnel, time and money is utilized as effective as possible.
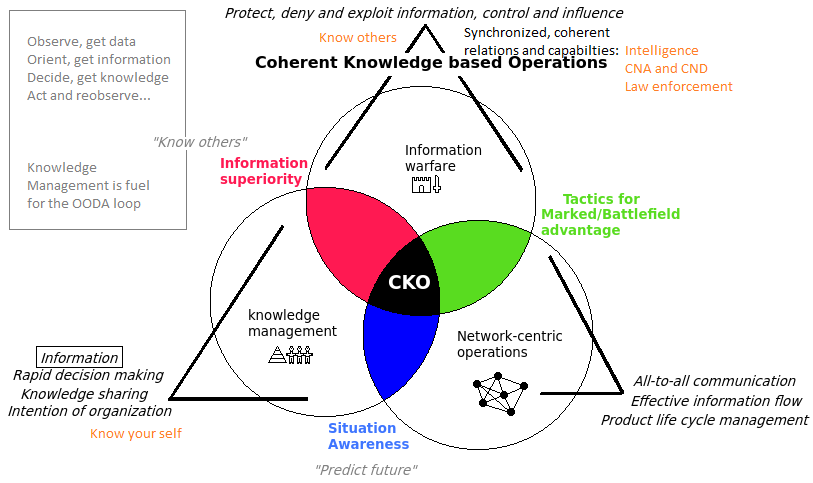
Based on information: Coherent and synchronized means to make others perform or not perform actions so that your own goals are achieved at the cost of the other parties. Protect, exploit, deny or destroy information itself or where it is hosted. Information Warfare
Global Information Warfare by Jones (2002) defines IW as Coherent and synchronized means of making others do or not do actions that benefit your agenda ... while protecting yourself from the opposite effect. This definition is flawed as a nuclear attack falls within the definition.
Making well informed decisions fast by means of sharing of information achieved by improving processes, culture and technology so that information can be shared efficiently cross geographical, organizational and personal boundaries. Knowledge Management
"How business is done". Collect, process and make decisions fast based on highly connected nodes as compared to rigid hierarchical structures with restrictions on information flow Network Centric "Operations"
The question then is: What is the difference between network centric operations and knowledge management? Isn't NCB/NCW just a subset of KM?
Knowledge management is an active stand towards information in an organization, where the value of it is in focus. Network centric thinking is basically to distribute information faster by utilizing networks of intelligence enforced by fast networked communication. The result can be Situation awareness. This might be because many heads can process the information in parallel and draw synergies because they all know the goal and has access to indicators. High situation awareness is a requirement for making good predictions.
Knowledge management combined with only Information warfare gives Information superiority. This term has not been defined, but the words indicate it has to do with being in control of information, being able to control it. Control involves use of force and protection against use of force, a component in information warfare. Knowledge management is the handling and awareness of information so none of them will give information superiority alone. The information must be controlled and processed/managed.
The third single pair is information warfare combined with network centric thinking. The result is basically ability to increased success in the marked/battlefield. Information superiority is not achieved because of lacking knowledge management, but fast networked processing resulting in quick decisions/actions or supply chain management combined with exploitation of information still leads to better chances in the domain of competition. Lack of knowledge management will lead to underutilized potential.
The CKO model strives for all tree domains, and the result is theorized as increasing the chances of gaining domain dominance (NC + IW) while minimizing underutilized potential (KM), predicting better and making decisions faster.
An interesting related source: Coherent Knowledge-based Operations (CKO) by Daniel Solstad